Multicluster LoadBalanced DNSPolicy¶
Terms¶
GatewayAPI: resources that model service networking in Kubernetes.Gateway: Kubernetes Gateway resource.ManagedZone: Kuadrant resource representing a Zone Apex in a dns provider.DNSPolicy: Kuadrant policy for managing gateway dns.DNSRecord: Kuadrant resource representing a set of records in a managed zone.
DNS Provider Setup¶
A DNSPolicy acts against a target Gateway by processing its listeners for hostnames that it can create dns records for. In order for it to do this, it must know about dns providers, and what domains these dns providers are currently hosting. This is done through the creation of ManagedZones and dns provider secrets containing the credentials for the dns provider account.
If for example a Gateway is created with a listener with a hostname of echo.apps.hcpapps.net:
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: prod-web
namespace: multi-cluster-gateways
spec:
gatewayClassName: kuadrant-multi-cluster-gateway-instance-per-cluster
listeners:
- allowedRoutes:
namespaces:
from: All
name: api
hostname: echo.apps.hcpapps.net
port: 80
protocol: HTTP
In order for the DNSPolicy to act upon that listener, a ManagedZone must exist for that hostnames domain.
A secret containing the provider credentials must first be created:
kubectl create secret generic my-aws-credentials --type=kuadrant.io/aws --from-env-file=./aws-credentials.env -n multi-cluster-gateways
kubectl get secrets my-aws-credentials -n multi-cluster-gateways -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: <AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID>
AWS_REGION: <AWS_REGION>
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: <AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY>
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: my-aws-credentials
namespace: multi-cluster-gateways
type: kuadrant.io/aws
And then a ManagedZone can be added for the desired domain referencing the provider credentials:
apiVersion: kuadrant.io/v1alpha1
kind: ManagedZone
metadata:
name: apps.hcpapps.net
namespace: multi-cluster-gateways
spec:
domainName: apps.hcpapps.net
description: "apps.hcpapps.net managed domain"
dnsProviderSecretRef:
name: my-aws-credentials
DNSPolicy creation and attachment¶
Once an appropriate ManagedZone is configured for a Gateways listener hostname, we can now create and attach a DNSPolicy to start managing dns for it.
apiVersion: kuadrant.io/v1alpha1
kind: DNSPolicy
metadata:
name: prod-web
namespace: multi-cluster-gateways
spec:
targetRef:
name: prod-web
group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
kind: Gateway
healthCheck:
allowInsecureCertificates: true
additionalHeadersRef:
name: probe-headers
endpoint: /
expectedResponses:
- 200
- 201
- 301
failureThreshold: 5
port: 80
protocol: http
Target Reference¶
targetRef field is taken from policy attachment's target reference API. It can only target one resource at a time. Fields included inside:
- Group is the group of the target resource. Only valid option is gateway.networking.k8s.io.
- Kind is kind of the target resource. Only valid options are Gateway.
- Name is the name of the target resource.
- Namespace is the namespace of the referent. Currently only local objects can be referred so value is ignored.
Health Check¶
The health check section is optional, the following fields are available:
allowInsecureCertificates: Added for development environments, allows health probes to not fail when finding an invalid (e.g. self-signed) certificate.additionalHeadersRef: A reference to a secret which contains additional headers such as an authentication tokenendpoint: The path to specify for these health checks, e.g./healthzexpectedResponses: Defaults to 200 or 201, this allows other responses to be considered validfailureThreshold: How many consecutive fails are required to consider this endpoint unhealthyport: The port to connect toprotocol: The protocol to use for this connection
For more information about DNS Health Checks, see this guide.
Checking status of health checks¶
To list all health checks:
This will list all probes in the hub cluster, and whether they are currently healthy or not.To find more information on why a specific health check is failing, look at the status of that probe:
DNSRecord Resources¶
The DNSPolicy will create a DNSRecord resource for each listener hostname with a suitable ManagedZone configured. The DNSPolicy resource uses the status of the Gateway to determine what dns records need to be created based on the clusters it has been placed onto.
Given the following Gateway status:
status:
addresses:
- type: kuadrant.io/MultiClusterIPAddress
value: kind-mgc-workload-1/172.31.201.1
- type: kuadrant.io/MultiClusterIPAddress
value: kind-mgc-workload-2/172.31.202.1
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2023-07-24T19:09:54Z"
message: Handled by kuadrant.io/mgc-gw-controller
observedGeneration: 1
reason: Accepted
status: "True"
type: Accepted
- lastTransitionTime: "2023-07-24T19:09:55Z"
message: 'gateway placed on clusters [kind-mgc-workload-1 kind-mgc-workload-2] '
observedGeneration: 1
reason: Programmed
status: "True"
type: Programmed
listeners:
- attachedRoutes: 1
conditions: []
name: kind-mgc-workload-1.api
supportedKinds: []
- attachedRoutes: 1
conditions: []
name: kind-mgc-workload-2.api
supportedKinds: []
The example DNSPolicy shown above would create a DNSRecord like the following:
apiVersion: kuadrant.io/v1alpha1
kind: DNSRecord
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2023-07-24T19:09:56Z"
finalizers:
- kuadrant.io/dns-record
generation: 3
labels:
kuadrant.io/Gateway-uid: 0877f97c-f3a6-4f30-97f4-e0d7f25cc401
kuadrant.io/record-id: echo
name: echo.apps.hcpapps.net
namespace: multi-cluster-gateways
ownerReferences:
- apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
name: echo-app
uid: 0877f97c-f3a6-4f30-97f4-e0d7f25cc401
- apiVersion: kuadrant.io/v1alpha1
blockOwnerDeletion: true
controller: true
kind: ManagedZone
name: apps.hcpapps.net
uid: 26a06799-acff-476b-a1a3-c831fd19dcc7
resourceVersion: "25464"
uid: 365bf57f-10b4-42e8-a8e7-abb6dce93985
spec:
endpoints:
- dnsName: 24osuu.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
recordTTL: 60
recordType: A
targets:
- 172.31.202.1
- dnsName: default.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
providerSpecific:
- name: weight
value: "120"
recordTTL: 60
recordType: CNAME
setIdentifier: 24osuu.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
targets:
- 24osuu.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
- dnsName: default.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
providerSpecific:
- name: weight
value: "120"
recordTTL: 60
recordType: CNAME
setIdentifier: lrnse3.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
targets:
- lrnse3.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
- dnsName: echo.apps.hcpapps.net
recordTTL: 300
recordType: CNAME
targets:
- lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
- dnsName: lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
providerSpecific:
- name: geo-country-code
value: '*'
recordTTL: 300
recordType: CNAME
setIdentifier: default
targets:
- default.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
- dnsName: lrnse3.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
recordTTL: 60
recordType: A
targets:
- 172.31.201.1
managedZone:
name: apps.hcpapps.net
Which results in the following records being created in AWS Route53 (The provider we used in our example ManagedZone above):
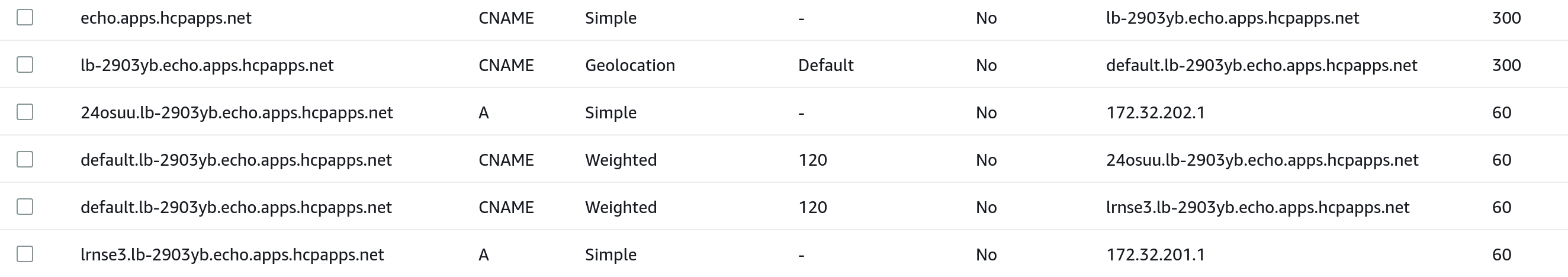
The listener hostname is now be resolvable through dns:
dig echo.apps.hcpapps.net +short
lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net.
default.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net.
lrnse3.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net.
172.31.201.1
More information about the dns record structure can be found in the DNSRecord structure document.
Load Balancing¶
Configuration of DNS Load Balancing features is done through the loadBalancing field in the DNSPolicy spec.
loadBalancing field contains the specification of how dns will be configured in order to provide balancing of load across multiple clusters. Fields included inside:
- weighted field describes how weighting will be applied to weighted dns records. Fields included inside:
- defaultWeight arbitrary weight value that will be applied to weighted dns records by default. Integer greater than 0 and no larger than the maximum value accepted by the target dns provider.
- custom array of custom weights to apply when custom attribute values match.
- geo field enables the geo routing strategy. Fields included inside:
- defaultGeo geo code to apply to geo dns records by default. The values accepted are determined by the target dns provider.
Weighted¶
A DNSPolicy with an empty loadBalancing spec, or with a loadBalancing.weighted.defaultWeight set and nothing else produces a set of records grouped and weighted to produce a Round Robin routing strategy where all target clusters will have an equal chance of being returned in DNS queries.
If we apply the following update to the DNSPolicy:
apiVersion: kuadrant.io/v1alpha1
kind: DNSPolicy
metadata:
name: prod-web
namespace: multi-cluster-gateways
spec:
targetRef:
name: prod-web
group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
kind: Gateway
loadBalancing:
weighted:
defaultWeight: 100 # <--- New Default Weight being added
The weight of all records is adjusted to reflect the new defaultWeight value of 100. This will still produce the same Round Robin routing strategy as before since all records still have equal weight values.
Custom Weights¶
In order to manipulate how much traffic individual clusters receive, custom weights can be added to the DNSPolicy.
If we apply the following update to the DNSPolicy:
apiVersion: kuadrant.io/v1alpha1
kind: DNSPolicy
metadata:
name: prod-web
namespace: multi-cluster-gateways
spec:
targetRef:
name: prod-web
group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
kind: Gateway
loadBalancing:
weighted:
defaultWeight: 120
custom: # <--- New Custom Weights being added
- weight: 255
selector:
matchLabels:
kuadrant.io/lb-attribute-custom-weight: AWS
- weight: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
kuadrant.io/lb-attribute-custom-weight: GCP
And apply custom-weight labels to each of our managed cluster resources:
kubectl label --overwrite managedcluster kind-mgc-workload-1 kuadrant.io/lb-attribute-custom-weight=AWS
kubectl label --overwrite managedcluster kind-mgc-workload-2 kuadrant.io/lb-attribute-custom-weight=GCP
The DNSRecord for our listener host gets updated, and the weighted records are adjusted to have the new values:
kubectl get dnsrecord echo.apps.hcpapps.net -n multi-cluster-gateways -o yaml | yq .spec.endpoints
- dnsName: 24osuu.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
recordTTL: 60
recordType: A
targets:
- 172.31.202.1
- dnsName: default.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
providerSpecific:
- name: weight
value: "10" # <--- Weight is updated
recordTTL: 60
recordType: CNAME
setIdentifier: 24osuu.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
targets:
- 24osuu.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
- dnsName: default.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
providerSpecific:
- name: weight
value: "255" # <--- Weight is updated
recordTTL: 60
recordType: CNAME
setIdentifier: lrnse3.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
targets:
- lrnse3.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
- dnsName: echo.apps.hcpapps.net
recordTTL: 300
recordType: CNAME
targets:
- lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
- dnsName: lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
providerSpecific:
- name: geo-country-code
value: '*'
recordTTL: 300
recordType: CNAME
setIdentifier: default
targets:
- default.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
- dnsName: lrnse3.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
recordTTL: 60
recordType: A
targets:
- 172.31.201.1

In the above scenario the managed cluster kind-mgc-workload-2 (GCP) IP address will be returned far less frequently in DNS queries than kind-mgc-workload-1 (AWS)
Geo¶
To enable Geo Load balancing the loadBalancing.geo.defaultGeo field should be added. This informs the DNSPolicy that we now want to start making use of Geo Location features in our target provider.
This will change the single record set group created from default (What is created for weighted only load balancing) to a geo specific one based on the value of defaultGeo.
If we apply the following update to the DNSPolicy:
apiVersion: kuadrant.io/v1alpha1
kind: DNSPolicy
metadata:
name: prod-web
namespace: multi-cluster-gateways
spec:
targetRef:
name: prod-web
group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
kind: Gateway
loadBalancing:
weighted:
defaultWeight: 120
custom:
- weight: 255
selector:
matchLabels:
kuadrant.io/lb-attribute-custom-weight: AWS
- weight: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
kuadrant.io/lb-attribute-custom-weight: GCP
geo:
defaultGeo: US # <--- New `geo.defaultGeo` added for `US` (United States)
The DNSRecord for our listener host gets updated, and the default geo is replaced with the one we specified:
kubectl get dnsrecord echo.apps.hcpapps.net -n multi-cluster-gateways -o yaml | yq .spec.endpoints
- dnsName: 24osuu.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
recordTTL: 60
recordType: A
targets:
- 172.31.202.1
- dnsName: echo.apps.hcpapps.net
recordTTL: 300
recordType: CNAME
targets:
- lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
- dnsName: lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net # <--- New `us` geo location CNAME is created
providerSpecific:
- name: geo-country-code
value: US
recordTTL: 300
recordType: CNAME
setIdentifier: US
targets:
- us.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
- dnsName: lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
providerSpecific:
- name: geo-country-code
value: '*'
recordTTL: 300
recordType: CNAME
setIdentifier: default
targets:
- us.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net # <--- Default catch all CNAME is updated to point to `us` target
- dnsName: lrnse3.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
recordTTL: 60
recordType: A
targets:
- 172.31.201.1
- dnsName: us.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net # <--- Gateway default group is now `us`
providerSpecific:
- name: weight
value: "10"
recordTTL: 60
recordType: CNAME
setIdentifier: 24osuu.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
targets:
- 24osuu.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
- dnsName: us.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net # <--- Gateway default group is now `us`
providerSpecific:
- name: weight
value: "255"
recordTTL: 60
recordType: CNAME
setIdentifier: lrnse3.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
targets:
- lrnse3.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net

The listener hostname is still resolvable, but now routed through the us record set:
dig echo.apps.hcpapps.net +short
lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net.
us.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net. # <--- `us` CNAME now in the chain
lrnse3.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net.
172.31.201.1
Configuring Cluster Geo Locations¶
The defaultGeo as described above puts all clusters into the same geo group, but for geo to be useful we need to mark our clusters as being in different locations.
We can do this though by adding geo-code attributes on the ManagedCluster to show which county each cluster is in. The values that can be used are determined by the dns provider (See Below).
Apply geo-code labels to each of our managed cluster resources:
kubectl label --overwrite managedcluster kind-mgc-workload-1 kuadrant.io/lb-attribute-geo-code=US
kubectl label --overwrite managedcluster kind-mgc-workload-2 kuadrant.io/lb-attribute-geo-code=ES
The above indicates that kind-mgc-workload-1 is located in the US (United States), which is the same as our current default geo, and kind-mgc-workload-2 is in ES (Spain).
The DNSRecord for our listener host gets updated, and records are now divided into two groups, us and es:
kubectl get dnsrecord echo.apps.hcpapps.net -n multi-cluster-gateways -o yaml | yq .spec.endpoints
- dnsName: 24osuu.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
recordTTL: 60
recordType: A
targets:
- 172.31.202.1
- dnsName: echo.apps.hcpapps.net
recordTTL: 300
recordType: CNAME
targets:
- lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
- dnsName: es.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net # <--- kind-mgc-workload-2 target now added to `es` group
providerSpecific:
- name: weight
value: "10"
recordTTL: 60
recordType: CNAME
setIdentifier: 24osuu.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
targets:
- 24osuu.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
- dnsName: lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net # <--- New `es` geo location CNAME is created
providerSpecific:
- name: geo-country-code
value: ES
recordTTL: 300
recordType: CNAME
setIdentifier: ES
targets:
- es.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
- dnsName: lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
providerSpecific:
- name: geo-country-code
value: US
recordTTL: 300
recordType: CNAME
setIdentifier: US
targets:
- us.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
- dnsName: lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
providerSpecific:
- name: geo-country-code
value: '*'
recordTTL: 300
recordType: CNAME
setIdentifier: default
targets:
- us.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
- dnsName: lrnse3.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
recordTTL: 60
recordType: A
targets:
- 172.31.201.1
- dnsName: us.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
providerSpecific:
- name: weight
value: "255"
recordTTL: 60
recordType: CNAME
setIdentifier: lrnse3.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
targets:
- lrnse3.lb-2903yb.echo.apps.hcpapps.net
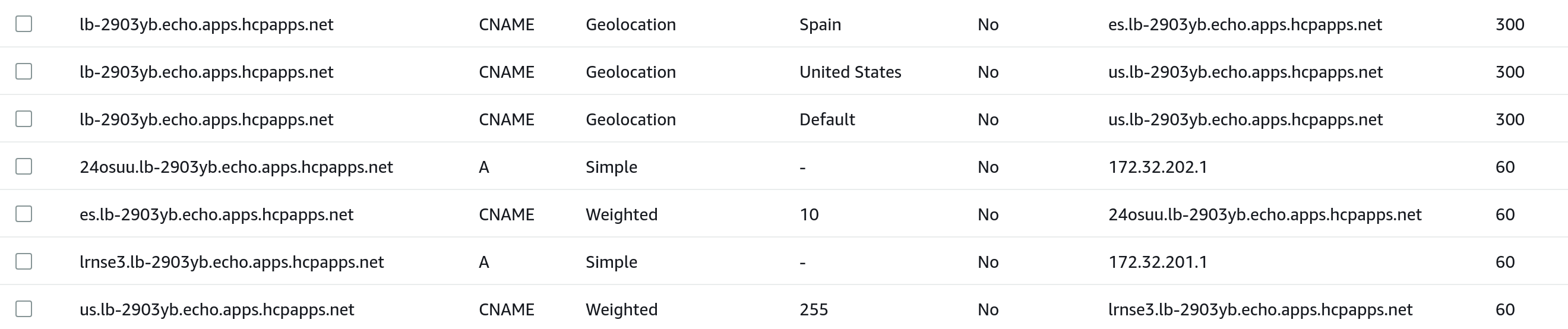
In the above scenario any requests made in Spain will be returned the IP address of kind-mgc-workload-2 and requests made from anywhere else in the world will be returned the IP address of kind-mgc-workload-1.
Weighting of records is still enforced between clusters in the same geo group, in the case above however they are having no effect since there is only one cluster in each group.

Locations supported per DNS provider¶
| Supported | AWS | GCP |
|---|---|---|
| Continents |  |
 |
| Country codes |  |
 |
| States |  |
 |
| Regions |  |
 |
Continents and country codes supported by AWS Route 53¶
:Note: 
To see all regions supported by AWS Route 53, please see the official (documentation)[https://docs.aws.amazon.com/Route53/latest/DeveloperGuide/resource-record-sets-values-geo.html]
Regions supported by GCP CLoud DNS¶
To see all regions supported by GCP Cloud DNS, please see the official (documentation)[https://cloud.google.com/compute/docs/regions-zones]